The global automotive industry is heading towards an intelligent inflection point, and a life-and-death game between computing power and thermodynamics is being staged. The Chinese market is leading this change with an astonishing acceleration - the market size of 449.5 billion yuan will account for 35%-45% of the global share in 2025, and will exceed 1.2 trillion yuan by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 30%. High-end intelligent driving (L3/L4 level) is becoming a new growth engine, driving continuous breakthroughs in technological boundaries.
In 2025, the penetration rate of L2 assisted driving in domestic passenger cars will reach 65%, and some new energy models (such as BYD and Wei Xiaoli) will be close to 90%, becoming a real "new car standard". The more revolutionary high-end intelligent driving is ushering in the ice-breaking commercialization: the penetration rate of L3 has exceeded 15%, and the coverage rate of urban NOA (automatic assisted navigation driving) function has climbed to 26.3%, marking a key leap from assistance functions to autonomous driving in intelligent driving.
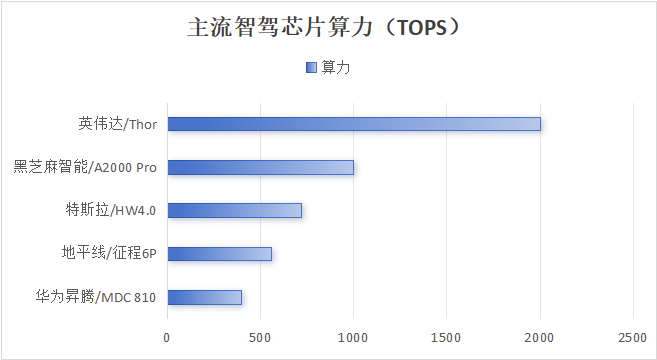
Figure The computing power of mainstream intelligent driving chips continues to improve (compiled by HFC based on public information)
1. The "hot" crisis of intelligent driving upgrades: computing power runs wildly and encounters physical limits
With the rush of intelligent driving technology, finer perception, more complex decision-making, and safer redundancy, every progress is frantically demanding computing power. From L2 to L4, the demand for computing power has skyrocketed: each generation upgrade requires 3-5 times the computing power reserve, and the demand for thousands of TOPS computing power has become the norm.
The impact of the breakthrough in intelligent driving computing power:
The dilemma of heat dissipation space: The power consumption of 1,000 TOPS chips exceeds 700W (equivalent to 5 PS5 game consoles), but the car has limited heat dissipation space.
Performance halving crisis: High temperature frequency reduction in a limited space may cause paper computing power to evaporate by 50% in actual scenarios.
Energy efficiency ratio life and death line: From 2024, the procurement indicators of car companies have shifted from "peak computing power" to "effective computing power per watt" (TOPS/W).
How to strike a balance between high power consumption and limited heat dissipation space will become a key intersection that determines the success or failure of technology implementation. Therefore, the ultimate competition of intelligent driving is not only in the algorithm code, but also between the "heat sink" and the chip.
Second, the ultimate battle of intelligent driving must win both algorithms and thermodynamics
High computing power will inevitably bring high power consumption, and hardware heat dissipation capacity seriously restricts the development of intelligent driving. Cooling challenges faced by intelligent driving chips:
The heat flux density brought about by high computing power has surged
Computing power requirements: L4/L5 autonomous driving requires 100-1000 TOPS computing power, and the chip power consumption can reach tens to hundreds of watts (such as NVIDIA Thor 730-2000 TOPS power consumption is about 90-280W).
Thermal accumulation: High computing power leads to a sharp increase in heat generation per unit area (chip heat flux density exceeds 100W/cm²), which is difficult for traditional heat dissipation solutions to cope with.
Dynamic heat load in complex scenarios
Computing fluctuations: Unexpected scenarios (such as emergency obstacle avoidance) trigger peak computing power, and instantaneous temperature spikes may trigger chip frequency reductions, affecting real-time performance.
Ambient temperature: The vehicle has a wide ambient temperature range (-40°C~120°C), and extreme conditions exacerbate the difficulty of heat dissipation.
Reliability requirements of vehicle specifications
Long-term stability: It needs to withstand temperature cycling, vibration, etc. during the 10-15 year life cycle, and the aging of heat dissipation materials may affect performance.
Safety: Overheating can cause the system to crash, directly threatening driving safety.
Space and integration limitations
Compact design: The chip needs to be highly integrated with sensors, power modules, etc., and the heat dissipation space is limited.
Multi-heat source interference: SOC, GPU, AI accelerators, etc. work together to achieve significant thermal coupling effects.
3. The key bottleneck of traditional thermal interface materials
L2-L3 intelligent driving chips mostly use thermal conductivity gel heat dissipation solutions with thermal conductivity of 5W~9W, but under the heat dissipation needs of high-power L3/L4 chips, this solution exposes core limitations.
Bottleneck of heat conduction performance: It is difficult to meet the demand for high power heat dissipation
Low thermal conductivity: Thermal conductivity (5-9 W/mK) is the core shortcoming of thermal conductive gels, which is obviously a bit inadequate under the continuous rise of chip power.
Thermal resistance layer thickness constraints: The thermal conductive gel needs to maintain a certain thickness (0.1mm) to maintain morphological stability and prevent pumping, but this significantly increases the thermal resistance at the interface and weakens the heat dissipation efficiency.
Long-term reliability deterioration: the risk of irreversible attenuation of performance
Drying and hardening: Under long-term high temperatures, the thermal conductive gel is prone to dry and hard contraction due to the volatilization of the carrier, losing elasticity and filling ability, resulting in a sharp increase in contact thermal resistance, deterioration or even failure of heat dissipation performance, and may crack and damage the thermal interface.
Pump-out effect: The viscoelastic properties of the thermal conductive gel cause it to "crawl" under stress, which is extruded from the interface gap, causing thermal resistance to rise and heat dissipation to decrease, and may contaminate the surrounding circuit.
In this way, the continuous soaring computing power and TDP have gradually failed to meet the cooling needs of L3 to L4 intelligent driving chips. Graphene thermal gaskets with very low thermal resistance and high reliability are the preferred solution.
4. HFC longitudinal graphene thermal conductivity gasket: a revolutionary solution that directly hits the pain points of intelligent driving heat dissipation
Solve the bottleneck of heat conduction performance
Ultra-high longitudinal thermal conductivity: HFC graphene thermal conductivity gasket builds a continuous thermal conductivity path through directional arrangement technology, with a thermal conductivity of up to 130W/mK, which is more than 10 times higher than traditional interface materials and 3 times higher than the best products in the market.
Ultra-thin and low thermal resistance: Through the ultra-thin process, up to 70% of the compression amount can be used, and the BLT in the TIM scenario of chip packaging can reach 0.1mm, and the appropriate packaging pressure is applied, and the thermal resistance is as low as 0.04°Ccm²/W.
Zero pumping out anti-deformation: Three-dimensional graphene skeleton support, no flow under high temperature/vibration, eliminating heat dissipation attenuation caused by thickness compromise.

Figure HFC graphene thermal conductivity gasket is composed of longitudinal continuous, high thermal conductivity, and low density graphene
Figure HFC graphene thermal conductivity gasket
2. Long-term reliability
Anti-creep structure: HFC graphene thermal conductive gasket uses vertically oriented graphene structure to achieve efficient thermal conduction, and its special internal structure design can release stress, inhibit creep, and maintain a stable and reliable interface after 1000 cold and hot cycles.
High reliability: It has passed the rigorous 1000h high temperature, high and low temperature impact, and double 85 aging tests of HFC's internal CNAS accreditation laboratory and mass production customer laboratory, and its reliability is significantly better than that of conventional thermal interface materials.
Permanent elasticity: -40°C~150°C maintains a rebound rate of >60% in the whole temperature range, and there is no dry crack shrinkage.
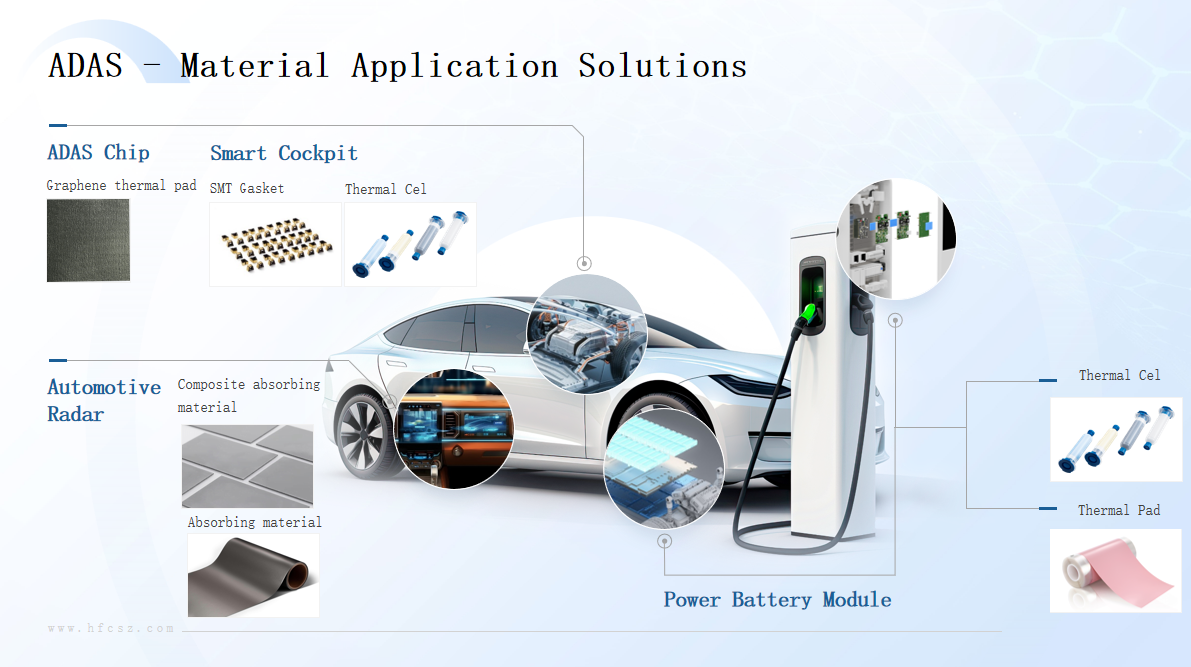
Figure HFC intelligent driving cooling solution
3. Market recognition at home and abroad
High-quality mass commercialization: HFC longitudinal graphene thermal conductive gasket has accumulated many years of experience in chip heat dissipation applications, and has achieved automated production lines and mass production delivery, and its product quality has been recognized by many leading enterprises in the chip industry at home and abroad and won the "Quality Excellence Award".
Independent innovation is the world's leader: HFC is a manufacturer of innovative EMC and thermal interface materials, longitudinal graphene gaskets have original process equipment and technical patents, and have a complete series of product intellectual property rights. It has laid out production bases in Shenzhen, Malaysia, Thailand and other places to meet the supply needs at home and abroad.
Copyright © Shenzhen HFC Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved | Sitemap | Technical Support 